БИБЛИОГРАФИЯ
Acemoglu, Daron, and David Autor 2011 “Skills, Tasks and Technologies Implications for Employment and Earnings “ In Orley Ashenfelter and David Card, eds, Handbook of Labor Economics, 4 1043–1171 Amsterdam Elsevier-North Holland.
Acemoglu, Daron, and James Robinson 2012 Why Nations Fail The Origins of Power, Prosperity, and Poverty Cambridge, MA Harvard Umver sity Press. (Дарен Аджемоглу, Джеймс Робинсон. Почему одни страны богатые, а другие бедные. Происхождение власти, процветания и нищеты. М.: Эксмо, 2017.)
Adler, Mortimer Jerome 1970 The Time of Our Lives The Ethics of Common Sense. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Akerlof, G , and R Kranton 2010 Identity Economics Princeton, NJ Princeton University Press. (Джордж Акерлоф, Рейчел Крэнтон. Экономика идентичности. Как наши идеалы и социальные нормы определяют, кем мы работаем, сколько зарабатываем и насколько несчастны. М: Карьера Пресс, 2010.)
Albert, Rika, Istvan Albert, and Gary L Nakarado 2004 “Structural Vulnerability of the North American Power Grid” Physical Review E 69 025103.
Allesina, Stefano, and Mercedes Pascual 2009 “Googling Food Webs: Can an Eigenvector Measure Species’ Importance for Coextmctions?” PLOS Computational Biology 9, no 4.
Allison, Graham 1971 Essence of Decision Explaining the Cuban Missile Crisis New York Little, Brown. (Алисон Грэм. Квинтэссенция решения. На примере Карибского кризиса 1962 года. М.: Едиториал УРСС, 2012.)
Alvaredo, Facundo, Anthony B Atkinson, Thomas Piketty, and Emmanuel Saez 2013 “The World Top Incomes Database” .
Anderson, Chris 2008a “The End of Theory The Data Deluge Makes the Scientific Method Obsolete“ Wired 16, no 7.
Anderson, Chris 2008b The Long Tail Why the Future of Business Is Selling Less of More New York Hachette Anderson, Phillip 1972 “More Is Different “ Science 177, no 4047 393–396.
Arrow, Kenneth, 1963. Social Choice and Individual Values. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. (Кеннет Эрроу. Коллективный выбор и индивидуальные ценности. М.: ГУ ВШЭ, 2004.)
Arthur, W. B. 1994. “Inductive Reasoning and Bounded Rationality (The El Farol Problem).” American Economic Review Papers and Proceedings 84: 406–411.
Arthur, W. B. 2011. The Nature of Technology: What It Is and How It Evolves. New York: Free Press.
Ashenfelter, Orley. 2010. “Predicting the Quality and Prices of Bordeaux Wine.” Journal of Wine Economics 5, no. 1: 40–52.
Athey, Susan, Jonathan Levin, and Enrique Seira. 2011. “Comparing Open and Sealed Bid Auctions: Evidence from Timber Auctions.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 126, no. 1: 207–257.
Austin, David. 2008. “Percolation: Slipping Through the Cracks.” American Mathematical Society, .
Axelrod, Robert. 1984. The Evolution of Cooperation. New York: Basic Books.
Axelrod, David, Robert Axelrod, and Kenneth J. Pienta. 2006. “Evolution of Cooperation Among Tumor Cells.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 103, no. 36: 13474–13479.
Axtell, Robert L. 2001. “Zipf Distribution of U.S. Firm Sizes.” Science 293: 1818–1820.
Bajari, Patrick, and Matthew E. Kahn. 2008. “Estimating Hedonic Models of Consumer Demand with an Application to Urban Sprawl.” In Hedonic Methods in Housing Markets, 129–155. New York: Springer.
Bak, Per. 1996. How Nature Works: The Science of Self-Organized Criticality. New York: Springer. (Бак Пер. Как работает природа. Теория самоорганизованной критичности. М.: Либроком, 2015.)
Baldwin, Carliss Y, and Kim B. Clark. 2000. Design Rules. Vol. 1, The Power of Modularity. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Ball, Eric, and Joseph LiPuma. 2012. Unlocking the Ivory Tower: How Management Research Can Transform Your Business. Palo Alto, CA: Kauffman Fellow Press.
Banzhaf, John F. 1965. “Weighted Voting Doesn’t Work: A Mathematical Analysis.” Rutgers Law Review 19, no. 2: 317–343.
Barber, Gerald M. 1997. “Sequencing Highway Network Improvements: A Case Study of South Sulawesi.” Economic Geography 53, no. 1: 55–69.
Bass, Frank. 1969. “A New Product Growth Model for Consumer Durables.” Management Science 15, no. 5: 215–227.
Baxter, G. William. 2009. “The Dynamics of Foraging Ants.” Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Physical Society, March 16–20, abstract H40.00011.
Bednar, Jenna. 2007. “Credit Assignment and Federal Encroachment.” Supreme Court Economic Review 15: 285–308.
Bednar, Jenna. 2008. The Robust Federation: Principle of Design. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Bednar, Jenna, Aaron Bramson, Andrea Jones-Rooy, and Scott E. Page. 2010. “Emergent Cultural Signatures and Persistent Diversity: A Model of Conformity and Consistency.” Rationality and Society 22, no. 4: 407–444.
Bednar, Jenna, and Scott E. Page. 2007. “Can Game(s) Theory Explain Culture? The Emergence of Cultural Behavior Within Multiple Games.” Rationality and Society 19, no. 1: 65–97.
Bednar, Jenna, and Scott E. Page. 2018. “When Order Affects Performance: Culture, Behavioral Spillovers and Institutional Path Dependence.” American Political Science Review 112, no. 1: 82–98.
Bell, Alex, Raj Chetty, Xavier Jaravel, Neviana Petkova, and John Van Reenen. 2018 “Who Becomes an Inventor in America? The Importance of Exposure to Innovation: Executive Summary.” .
Bendor, Jonathan, Daniel Diermeier, and Michael Ting. 2003. ‘A Behavioral Model of Turnout.” American Political Science Review 97, no. 2: 261–280.
Bendor, Jonathan, and Piotr Swistak. 1997. “The Evolutionary Stability of Cooperation.” American Political Science Review 91: 290–307.
Bendor, Jonathan, and Scott E. Page. 2018. “A Model of Team Problem Solving.” Неопубликованная рукопись.
Berg, Nathan, and Gerd Gigerenzer. 2010. ‘As-If Behavioral Economics: Neoclassical Economics in Disguise?” History of Economic Ideas 18, no. 1: 133–166.
Bergemann, Dirk, and Juuso Valimaki. 2008. “Bandit Problems.” In The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd ed., ed. Steven N. Durlauf and Lawrence E. Blume. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Berlekamp, Elwyn R., John H. Conway, and Richard K. Guy. 1982. “What Is Life?” In Winning Ways for Your Mathematical Plays. Vol. 2, Games in Particular. London: Academic Press.
Bertrand, Marianne, and Sendhil Mullainathan. 2001. “Are CEOs Rewarded for Luck? The Ones Without Principles Are.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 116: 901–932.
Bickel, P. J., E. A. Hammel, and J. W. O’Connell. 1974. “Sex Bias in Graduate Admissions: Data from Berkeley.” Science 187 (4175): 398–404.
Biernaskie, Jay, M. 2011. “Evidence for Competition and Cooperation Among Climbing Plants.” Proceedings of the Royal Society B 278: 1989–1996.
Bird, Rebecca, and Eric Smith. 2004. “Signaling Theory, Strategic Interaction, and Symbolic Capital.” Current Anthropology 46, no. 2: 222–248.
Boldrin, Michele, and David Levine. 2010. Against Intellectual Monopoly. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Borges, Jorge Luis. 1974. A Universal History of Infamy. Trans. Norman Thomas de Giovanni. London: Penguin. (Хорхе Луис Борхес. Всемирная история низости. М.: Амфора, 2006.)
Bowers, Jake, Nathaniel Higgins, Dean Karlan, Sarah Tulman, and Jonathan Zinman. 2017. “Challenges to Replication and Iteration in Field Experiments: Evidence from Two Direct Mail Shots.” American Economic Review Papers & Proceedings 107, no. 5: 1–3.
Bowles, Samuel, and Herbert Gintis. 2002. “The Inheritance of Inequality.” Journal of Economic Perspectives 16, no. 3: 3–30.
Box, George E. P., and Norman Draper. 1987. Empirical Model-Building and Response Surfaces. New York: Wiley.
Boyd, Robert. 2006. “Reciprocity: You Have to Think Different.” Journal of Evolutionary Biology 19: 1380–1382.
Breiman, Leo. 1996. “Bagging Predictors.” Machine Learning 24, no. 2: 123–140.
Briggs, Andrew, and Mark Sculpher. 1998. “An Introduction to Markov Modeling for Economic Evaluation.” Pharmaco Economics 13, no. 4: 397–409.
Brock, William, and Steven Durlauf. 2001. “Discrete Choice with Social Interactions.” Review of Economic Studies 68: 235–260.
Broido, A. D., and A. Clauset. 2018. “Scale-Free Networks Are Rare” (рабочий доклад).
Bshary, R., and A. S. Grutter. 2006. “Image Scoring and Cooperation in a Cleaner Fish Mutualism.” Nature 441, no. 7096: 975–978.
Burt, Ronald. 1995. Structural Holes: The Social Structure of Competition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Bush, Robert, and Frederick Mosteller. 1954. Stochastic Models for Learning. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Camerer, Colin F. 2003. Behavioral Game Theory: Experiments in Strategic Interaction. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Camerer, Colin, Linda Babcock, George Loewenstein, and Richard Thaler. 1997. “Labor Supply of New York City Cabdrivers: One Day at a Time.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 112, no. 2: 407–441.
Camerer, Colin, and Tek Ho. 1999. “Experience-Weighted Attraction Learning in Normal Form Games.” Econometrica 67, no. 4: 827–874.
Camerer, Colin, George Loewenstein, and Drazen Prelec. 2005. “Neuroe-conomics: How Neuroscience Can Inform Economics.” Journal of Economic Literature 43: 9–64.
Campbell, Donald T. 1976. “Assessing the Impact of Planned Social Change.” Public Affairs Center, Dartmouth College.
Campbell, James E., Bryan J. Dettrey, and Hongxing Yin. 2010. “The Theory of Conditional Retrospective Voting: Does the Presidential Record Matter Less in Open-Seat Elections?” Journal of Politics 72, no. 4: 1083–1095.
Cancian, Maria, and Deborah Reed. 1999. “The Impact of Wives’ Earnings on Income Inequality: Issues and Estimates.” Demography 36, no. 2: 173–184.
Carvalho, Vasco, and Xavier Gabaix. 2013 “The Great Diversification and Its Undoing,” American Economic Review 103, no. 5: 1697–1727.
Castellano, Claudio, Santo Fortunate, and Vittorio Loreto. 2009. “Statistical Physics of Social Dynamics.” Review of Modern Physics 81: 591–646.
Cederman, Lars Erik. 2003. “Modeling the Size of Wars: From Billiard Balls to Sandpiles.” American Political Science Review 97: 135–150.
Centola, Damon, and Michael Macy. 2007. “Complex Contagions and the Weakness of Long Ties.” American Journal of Sociology 113: 702–734.
Chance, Donald. 2009. “What Are the Odds? Another Look at DiMaggio’s Streak.” Chance 22, no. 2: 33–42.
Christakis, N. A., and J. Fowler. 2009. Connected: The Surprising Power of Our Social Networks and How They Shape Our Lives. New York: Little, Brown. (Николас Кристакис, Джеймс Фаулер. Связанные одной сетью. Как на нас влияют люди, которых мы никогда не видели. М.: Юнайтед Пресс, 2014.)
Churchland, Patricia, and Terry J. Sejnowski. 1992. The Computational Brain. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Chwe, Michael. 2013. Jane Austen: Game Theorist. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Clarida, Richard, Jordi Gall, and Mark Gertler. 2000. “Monetary Policy Rules and Macroeconomic Stability: Evidence and Some Theory.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 115, no. 1: 147–180.
Clark, Gregory. 2014. The Son Also Rises: Surnames and the History of Social Mobility. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. (Грегори Кларк. Отцы и дети. Фамилии и история социальной мобильности. М.: Издательство Института Гайдара, 2018.)
Clark, William, Matt Golder, and Sona Nadenicheck Golder. 2008. Principles of Comparative Politics. Washington, DC: Congressional Quarterly Press.
Clauset, Aaron, M. Young, and K. S. Gleditsch. 2007. “On the Frequency of Severe Terrorist Attacks.” Journal of Conflict Resolution 51, no. 1: 58–88.
Cohen, Tyler. 2013. Average Is Over: Powering America Beyond the Age of the Great Stagnation. New York: Dutton. (Тайлер Коуэн. Среднего более не дано. Как выйти из эпохи Великой стагнации. М.: Издательство Института Гайдара, 2015.)
Cooke, Nancy J., and Margaret L. Hilton, eds. 2014. Enhancing the Effectiveness of Team Science. Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
Cornes, Richard, and Todd Sandler. 1996. The Theory of Externalities, Public Goods, and Club Goods. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Craine, Joseph, and Ray Dybzinski. 2013. “Mechanisms of Plant Competition for Nutrients, Water and Light.” Functional Ecology 27: 833–840.
Cyert, Richard M., and James G. March. 1963. A Behavioral Theory of the Firm. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Dan, Avi. 2018. “How Michelle Peluso Is Redefining Marketing at IBM.” Forbes, January 18.
Dann, Carrie. 2016. “Pro-Clinton Battleground Ad Spending Outstrips Trump Team by 2.” NBC News, November 4.
Dawes, Robyn. 1979. “The Robust Beauty of Improper Linear Models in Decision Making.” American Psychologist 34: 571–582.
de Marchi, Scott. 2005. Computational and Mathematical Modeling in the Social Sciences. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
DeMiguel, Victor, Lorenzo Garlappi, and Raman Uppal. 2009. “Optimal Versus Naive Diversification: How Inefficient Is the 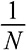 Portfolio Strategy?” Review of Financial Studies 22, no. 5: 1915–1953.
Portfolio Strategy?” Review of Financial Studies 22, no. 5: 1915–1953.
Dennett, Daniel C. 1991. Consciousness Explained. Boston: Back Bay Books.
Dennett, Daniel C. 1994. Darwin’s Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meanings of Life. New York: Simon & Schuster.
Denrell, Jerker, and Chengwei Liu. 2012. “Top Performers Are Not the Most Impressive When Extreme Performance Indicates Unreliability.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 109, no. 24: 9331–9336.
Diamond, Jared. 2005. Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed. New York: Viking Penguin. (Джаред Даймонд. Коллапс. Почему одни общества приходят к процветанию, а другие — к гибели. М.:АСТ, 2008.)
Dodds, Peter, Robby Muhamad, and Duncan Watts. 2003. ‘An Experimental Study of Search in Global Social Networks.” Science 301: 827–829.
Downing, John A., et al. 2006. “The Global Abundance and Size Distribution of Lakes, Ponds, and Impoundments.” Limnology and Oceanography 51, no. 5: 2388–2397.
Downs, Anthony. 1957. An Economic Theory of Democracy. New York: Harper.
Dragulescu, Adrian, and Victor M. Yakovenko. 2001. “Exponential and Power-Law Probability Distributions of Wealth and Income in the United Kingdom and the United States.” Physica A 299: 213–221.
Drucker, Peter. 1969. The Age of Discontinuity: Guidelines to Our Changing Society. New York: Harper and Row. (Питер Друкер. Эпоха разрыва. Ориентиры для нашего меняющегося общества. М.: Вильямс, 2007.)
Dubos, Jean. 1987. The White Plague: Tuberculosis, Man and Society. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
Dunne, Anthony. 1999. Hertzian Tales: Electronic Products, Aesthetic Experience and Critical Design. London: Royal College of Art.
Dyson, Freeman. 2004. ‘A Meeting with Enrico Fermi.” Nature 427: 297.
Easley, David, and Jon Kleinberg. 2010. Networks, Crowds, and Markets: Reasoning About a Highly Connected World. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Easley, David, Marcos Lopez de Prado, and Maureen O’Hara. 2012. “Flow Toxicity and Liquidity in a High Frequency World.” Review of Financial Studies 24, no. 5: 1457–1493.
Easterly, William, and Stanley Fischer. 1995. “The Soviet Economic Decline.” World Bank Economic Review 9, no. 3: 341–371.
Ebbinghaus, Herman. 1885. Memory: A Contribution to Experimental Psychology. Online in Classics in the History of Psychology. .
Ehrenberg, Andrew. 1969. “Towards an Integrated Theory of Consumer Behaviour.” Journal of the Market Research Society 11, no. 4: 305–337.
Einstein, Albert. 1934. “On the Method of Theoretical Physics.” Philosophy of Science 1, no. 2: 163–169.
Eliot, Matt, Ben Golub, and Matthew Jackson. 2014. “Financial Networks and Contagion.” American Economic Review 104, no. 10: 3115–3153.
Eom, Young-Ho, and Hang-Hyun Jo. 2014. “Generalized Friendship Paradox in Complex Networks: The Case of Scientific Collaboration.” Scientific Reports 4: 4603.
Epstein, Josh. 2006. Generative Social Science: Studies in Agent-Based Computational Modeling. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Epstein, Joshua. 2008. “Why Model?” Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 11, no. 4: 12.
Epstein, Joshua. 2014. Agent Zero: Toward Neurocognitive Foundations for Generative Social Science. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Ericsson, K. A. 1996. “The Acquisition of Expert Performance: An Introduction to Some of the Issues.” In The Road to Excellence: The Acquisition of Expert Performance in the Arts and Sciences, Sports, and Games, ed. K. A. Ericsson, 1–50. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Fair, Raymond. 2012. Predicting Presidential Elections and Other Things. 2nd ed. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Farmer, J. Doyne 2018. “Collective Awareness: A Conversation with J. Doyne Farmer.” The Edge. .
Feld, Scott L. 1991. “Why Your Friends Have More Friends than You Do.” American Journal of Sociology 96, no. 6: 1464–1477.
Flegal, Katherine M., Brian K. Kit, Heather Orpana, and Barry I. Graubard. 2012. “Association of All-Cause Mortality with Overweight and Obesity Using Standard Body Mass Index Categories: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.” Journal of the American Medical Association 309, no. 1: 71–82.
Flores, Thomas, and Irfan Nooruddin. 2016. Elections in Hard Times: Building Stronger Democracies in the 21st Century. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Florida, Richard. 2005. Cities and the Creative Class. New York: Routledge.
Foster, Dean, and H. Peyton Young. 2001. “On the Impossibility of Predicting the Behavior of Rational Agents.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 98, no. 22: 12848–12853.
Frank, Kenneth, et al. 2018. “Teacher Networks and Educational Opportunity.” In Handbook on the Sociology of Education, ed. Barbara Schneider and Guan Saw. New York: Oxford University Press.
Frank, Robert. 1985. Choosing the Right Pond. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Frank, Robert. 1996. The Winner-Take-All Society: Why the Few at the Top Get So Much More than the Rest of Us. New York: Penguin.
Freeman, Richard, and Wei Huang. 2015. “Collaborating with People Like Me: Ethnic Co-authorship Within the U.S.” Journal of Labor Economics 33 no. SI: S289–S318.
Fudenberg, Drew, and David Levine. 1998. Theory of Learning in Games. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Fudenberg, Drew, and David Levine. 2006. “A Dual-Self Model of Impulse Control.” American Economic Review 96: 1449–1476.
Gammill, James F., Jr., and Terry A. Marsh. 1988. “Trading Activity and Price Behavior in the Stock and Stock Index Futures Markets in October 1987.” Journal of Economic Perspectives 2, no. 3: 25–44.
Gawande, Atul. 2009. The Checklist Manifesto: How to Get Things Right. New York: Henry Holt. (Атул Гаванде. Чек-лист. Как избежать глупых ошибок, ведущих к фатальным последствиям. М.: Альпина Паблишер, 2014.)
Geithner, Timothy. 2014. Stress Test: Reflections on Financial Crises. New York: Crown.
Gerschenkron, Alexander. 1952. “Economic Backwardness in Historical Perspective.” In The Progress of Underdeveloped Areas, ed. B. F. Hoselitz. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Gertner, Jon. 2012. The Idea Factory: Bell Labs and the Great Age of American Innovation. New York: Penguin.
Gibrat, Robert. 1931. Les inegalites economique. Paris: Sirely.
Gigerenzer, Gerd, and Reinhard Selten. 2002. Bounded Rationality: The Adaptive Toolbox. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Gigerenzer, Gerd, and Peter Todd. 2000. Simple Heuristics That Make Us Smart. New York: Oxford University Press.
Gilboa, Itzhak, and David Schmeidler. 1994. “Case-Based Decision Theory.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 110: 605–639.
Gilovich, Thomas, Amos Tversky, and R. Vallone. 1984. “The Hot Hand in Basketball: On the Misperception of Random Sequences.” Cognitive Psychology 17, no. 3: 295–314.
Gittins, J., Jones, D. 1972. A dynamic allocation index for sequential design of experiments. In Progress in statistics, European Meeting of Statisticians (Vol. 1, pp. 241–266).
Glaeser, Edward, Bruce Sacerdote, and Jose Scheinkman. 1996. “Crime and Social Interactions.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 111, no. 2: 507–548.
Glantz, Andrew. 2008. “A Tax on Light and Air: Impact of the Window Duty on Tax Administration and Architecture, 1696–1851.” Penn History Review 15, no. 2: 18–40.
Glasserman, Paul, and H. Peyton Young. 2014. “Contagion in Financial Networks.” Office of Financial Research Working Paper.
Godard, Renee. 1993. “Tit for Tat Among Neighboring Hooded Warblers.” Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 33, no. 1: 45–50.
Gode, Dhananjay K., and Shyam Sunder. 1993. ‘Allocative Efficiency of Markets with Zero-Intelligence Traders: Market as a Partial Substitute for Individual Rationality.” Journal of Political Economy 101, no. 1: 119–137.
Goldin, Claudia, and Lawrence F. Katz. 2008. The Race Between Education and Technology. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Gordon, Robert J. 2016. The Rise and Fall of American Growth: The U.S. Standard of Living Since the Civil War. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Granovetter, Mark. 1973. “The Strength of Weak Ties.” American Journal of Sociology 78, no. 6: 1360–1380. (Марк Грановеттер. Сила слабых связей. —Экономическая социология. Сентябрь 2009.)
Granovetter, Mark. 1978. “Threshold Models of Collective Behavior.” American Journal of Sociology 83, no. 6: 1360–1443.
Greenwood, Jeremy, Nezih Guner, Georgi Kocharkov, and Cezar Santos. 2014. “Marry Your Like: Assortative Mating and Income Inequality.” American Economic Review: Papers & Proceedings 104, no 5: 348–353.
Greif, Avner. 2006. Institutions and the Path to the Modern Economy: Lessons from Medieval Trade. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. (Авнер Грейф. Институты и путь к современной экономике. Уроки средневековой торговли. М.: Издательский дом Высшей школы экономики, 2013.)
Griliches, Zvi. 1957, 1988. “Hybrid Corn: An Exploration of the Economics of Technological Change.” In Technology, Education and Productivity: Early Papers with Notes to Subsequent Literature. New York: Basil Black-well.
Groseclose, Tim, and James Snyder. 1996. “Buying Supermajorities.” American Political Science Review 90: 303–315.
Grossman, S., and J. Stiglitz. 1980. “On the Impossibility of Informationally Efficient Markets.” American Economic Review 70, no. 3: 393–408.
Groysberg, Boris. 2012. Chasing Stars: The Myth of Talent and the Portability of Performance. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Guy, Richard. 1983. “Don’t Try to Solve These Problems.” American Mathematical Monthly 90: 35–41.
Haidt, Jonathan. 2006. The Happiness Hypothesis: Finding Modern Truth in Ancient Wisdom. Basic Books. New York: NY.
Haldene, Andrew. 2012. “The Dog and the Frisbee.” Speech given at the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City’s 36th Economic Policy Symposium, Jackson Hole, WY.
Haldene, Andrew. 2014. “The Dappled World.” Speech given at the University of Michigan Law School, Ann Arbor, October 23.
Haldane, John B. S. 1928. “On Being the Right Size.” Интернет-версия доступна здесь: .
Hardin, Garret. 1968. “The Tragedy of the Commons.” Science 162, no. 3859: 1243–1248.
Harrell, Frank E. 2001. Regression Modeling Strategies with Applications to Linear Models, Logistic Regression, and Survival Analysis. New York: Springer.
Harstad, Ronald M., and Reinhard Selten. 2013. “Bounded Rationality Models: Tasks to Become Intellectually Competitive.” Journal of Economic Literature 51, no. 2: 496–511.
Harte, John. 1988. Consider a Spherical Cow. Mill Valley, CA: University Science Books.
Hathaway, Oona. 2001. “Path Dependence in the Law: The Course and Pattern of Change in a Common Law Legal System.” Iowa Law Review 86.
Havel, Vaclav. 1985. The Power of the Powerless: Citizens Against the State in Central-Eastern Europe. Ed. John Keane. Armonk, NY: M. E. Sharpe. (Вацлав Гавел. Сила бессильных. — Минск: Полифакт, 1991.)
Hawking, Stephen, and Leonard Mlodinow. 2011. The Grand Design. New-York: Bantam. (Стивен Хокинг, Леонард Млодинов. Высший замысел. М.: АСТ, 2017.)
Hecht, Jeff. 2008. “Prophecy of Economic Collapse ‘Coming True.’” New Scientist. November 17.
Herrnstein, Richard J. 1970. “On the Law of Effect.” Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior 13: 243–266.
Hills, Thomas, Peter M. Todd, David Lazer, A. David Redish, Iain D. Couzin, and the Cognitive Search Research Group. 2015. “Exploration Versus Exploitation in Space, Mind, and Society.” Trends in Cognitive Science 19, no. 1: 46–54.
Hofstadter, Douglas, and Emmanuel Sander. 2013. Surfaces and Essences: Analogy as the Fuel and Fire of Thinking. New York: Basic Books.
Holland, John. 1975. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
Hong, Lu, and Scott E. Page. 2009. “Interpreted and Generated Signals.” Journal of Economic Theory 144: 2174–2196.
Hotelling, Harold. 1929. “Stability in Competition.” Economic Journal 39, no. 153: 41–57.
Huffaker, Carl Burton. 1958. “Experimental Studies on Predation: Dispersion Factors and Predator-Prey Oscillations.” Hilgardia 27, no. 14: 343–383.
Hurwicz, Leo, and David Schmeidler. 1978. “Outcome Functions Which Guarantee the Existence and Pareto Optimality of Nash Equilibria.” Econometrica 46: 144–174.
Inman, Mason. 2011. “Sending Out an SOS.” Nature Climate Change 1: 180–183.
International Monetary Fund. 2009. Global Financial Stability Report.
Jackson, Matthew. 2008. Social and Economic Networks. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Jackson, Matthew and Asher Wolinsky. 1996. “A Strategic Model of Social and Economic Networks.” Journal of Economic Theory 71: 44–74.
Jacob, Francois. 1977. “Evolution and Tinkering.” Science 196: 1161–1166.
Jacobs, Jane. 1989. Revolving Doors: Sex Segregation and Women’s Careers. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Johnson, James. 2014. “Models Among the Political Theorists.” American Journal of Political Science 58, no. 33: 547–560.
Johnson-Laird, Philip. 2009. How We Reason. New York: Oxford University Press.
Jones, Benjamin E, Brian Uzzi, and Stefan Wuchty. 2008. “Multi-University Research Teams: Shifting Impact, Geography and Social Stratification in Science.” Science 322: 1259–1262.
Jones, Charles, and Jihee Kim. 2018 “A Schumpeterian Model of Top Income Inequality.” Journal of Political Economy. Готовится к публикации.
Kahneman, Daniel. 2011. Thinking Fast and Slow. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. (Даниэль Канеман. Думай медленно… решай быстро. М.: АСТ, Neoclassic, 2017.)
Kahneman, Daniel, and Amos Tversky. 1979. “Prospect Theory: An Analysis of Decisions Under Risk.” Econometrica 47, no. 2: 263–291. (Канеман Д. and Тверски А. Теория перспектив: анализ принятия решений в условиях риска. Журнал Экономика и математические методы (ЭММ), 2015, vol. 51, issue 1, 3-25.)
Kalyvas, Stathis. 1999. “The Decay and Breakdown of Communist One-Party Systems.” Annual Review of Political Science 2: 323–343.
Kamin, Leon J. 1969. “Predictability, Surprise, Attention and Conditioning.” In Punishment andAversive Behavior, ed. B. A. Campbell and R. M. Church, 279–296. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Kaplan, Steven, and Joshua D. Rauh. 2013a. “Family, Education, and Sources of Wealth Among the Richest Americans, 1982–2012.” American Economic Review Papers and Proceedings 103, no. 3: 158–162.
Kaplan, Steven, and Joshua D. Rauh. 2013b. “It’s the Market: The Broad-Based Rise in the Return to Top Talent.” Journal of Economic Perspectives 27, no. 3: 35–56.
Karlsson, Bengt. 2016. “The Forest of Our Lives: In and Out of Political Ecology.” Conservation and Society 14, no. 4: 380–390.
Kauffman, Stuart. 1993. The Origins of Order: Self-Organization and Selection in Evolution. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Kennedy, John F. 1956. Profiles in Courage. New York: Harper & Brothers. (Джон Ф. Кеннеди. Профили мужества. М.: Международные отношения, 2013.)
Khmelev, Dmitri, and E J. Tweedie. 2001. “Using Markov Chains for Identification of Writers.” Literary and Linguistic Computing 16, no. 4: 299–307.
Kleinberg, Jon, and M. Raghu. 2015. “Team Performance with Test Scores.” Working paper, Cornell University School of Information.
Knox, Grahame. n.d. “Lost at Sea.” Insight, .
Kollman, Ken, J. Miller, and S. Page. 1992. “Adaptive Parties in Spatial Elections.” American Political Science Review 86: 929–937.
Kooti, Farshad, Nathan O. Hodas, and Kristina Lerman. 2014. “Network Weirdness: Exploring the Origins of Network Paradoxes.” Работа представлена на Международной конференции блогов и социальных медиа (International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, ICWSM) в марте.
Kurlansky, Mark. 1998. Cod: A Biography of the Fish That Changed the World. New York: Penguin.
Kydland, Finn E., and Edward C. Prescott. 1977. “Rules Rather than Discretion: The Inconsistency of Optimal Plans.” Journal of Political Economy 85, no. 3: 473–491.
Lai, T. L, and Herbert Robbins. 1985. ‘Asymptotically Efficient Adaptive Allocation Rules.” Advances in Applied Mathematics 6, no. 1: 4–22.
Laibson, David. 1997. “Golden Eggs and Hyperbolic Discounting.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 112, no. 2: 443–477.
Lamberson, P J., and Scott E. Page. 2012a. “The Effect of Feedback Variability on Success in Markets with Positive Feedbacks.” Economics Letters 114: 259–261.
Lamberson, E J., and Scott E. Page. 2012b. “Tipping Points.” Quarterly Journal of Political Science 7, no. 2: 175–208.
Lancaster, Kelvin J. 1966. “A New Approach to Consumer Theory.” Journal of Political Economy 74: 132–157.
Landemore, Helene. 2013. Democratic Reason: Politics, Collective Intelligence, and the Rule of the Many. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Lango, Allen H., et al. 2010. “Hundreds of Variants Clustered in Genomic Loci and Biological Pathways Affect Human Height.” Nature 467, no. 7317: 832–838.
Langville, Amy N., and Carl D. Meyer. 2012. Who’s #1 ?: The Science of Rating and Ranking. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Lave, Charles, and James G. March. 1975. An Introduction to Models in the Social Sciences. Lanham, MD: University Press of America.
Ledyard, John, David Porter, and Antonio Rangle. 1997. “Experiments Testing Multiobject Allocation Mechanisms.” Journal of Economics and Management Strategy 6, no. 3: 639–675.
Ledyard, John, David Porter, and Randii Wessen. 2000. “A Market-Based Mechanism for Allocating Space Shuttle Secondary Payload Priority.” Experimental Economics 2, no. 3: 173–195.
Levins, Richard. 1966. “The Strategy of Model Building in Population Biology.” American Scientist 54: 421–431.
Levinthal, Daniel A. 1997. “Adaptation on Rugged Landscapes.” Management Science 43: 934–950.
Levinthal, Daniel. 1991. “Random Walks and Organizational Mortality.»Administrative Science Quarterly 36, no. 3: 397–420.
Levitt, Steven, and Stephen Dubner. 2009. SuperFreakonomics: Global Cooling, Patriotic Prostitutes, and Why Suicide Bombers Should Buy Life Insurance. New York: William Morrow. (Левитт С., Дабнер С. М. : Манн, Иванов и Фербер, 2010.)
Lewis, Michael. 2014. Flash Boys: A Wall Street Revolt. New York: W. W. Norton. (Майкл Л.. Flash Boys. Высокочастотная революция на Уолл-стрит. М. : Альпина Паблишер, 2019.)
Limpert, Eckhard, Werner A. Stahel, and Markus Abbt. 2001. “Log-normal Distributions Across the Sciences: Keys and Clues.” BioScience 51, no. 5: 341–352.
Little, Daniel. 1998. Microfoundations, Method, and Causation: On the Philosophy of the Social Sciences. Piscataway, NJ: Transaction Publishers.
Lo, Andrew W, and A. Craig MacKinlay. 2007. A Non-Random Walk Down Wall Street. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Lo, Andrew W 2012. “Reading About the Financial Crisis: A Twenty-One-Book Review.” Journal of Economic Literature 50, no. 1: 151–178.
Lucas, Robert. 1976. “Econometric Policy Evaluation: A Critique.” In The Phillips Curve and Labor Markets, ed. K. Brunner and A. Meltzer, 19–46. Carnegie-Rochester Conference Series on Public Policy 1. New York: Elsevier.
Lucking-Reiley, David. 1999. “Using Field Experiments to Test Equivalence Between Auction Formats: Magic on the Internet.” American Economic Review 89, no. 5: 1063–1080.
MacKenzie, Debora. 2012. “Boom and Doom: Revisiting Prophecies of Collapse.” New Scientist, January.
Mannes, Albert E., Jack B. Soil, and Richard E Larrick. 2014. “The Wisdom of Select Crowds.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 107: 276–299.
Markowitz, Harold M. 1952. “Portfolio Selection.” Journal of Finance 7, no. 1: 77–91.
Markus, Greg B. 1988. “The Impact of Personal and National Economic Conditions on the Presidential Vote: A Pooled Cross-Sectional Analysis.” American Journal of Political Science 32: 137–154.
Martin, Andrew D., and Kevin M. Quinn. 2002. “Dynamic Ideal Point Estimation via Markov Chain Monte Carlo for the U.S. Supreme Court, 1953–1999.” Political Analysis 10: 134–153.
Martin, Francis, et al. 2008. “The Genome of Laccana Bicolor Provides Insights into Mycorrhizal Symbiosis.” Nature 452: 88–92.
Martinez Peria, Maria Soledad, Giovanni Majnoni, Matthew T. Jones, and Winfrid Blaschke. 2001. “Stress Testing of Financial Systems: An Overview of Issues, Methodologies, and FSAP Experiences.” IMF Working Paper no. 01/88.
Mas-Colell, Andreu, Michael D. Whinston, and Jerry R. Green. 1994. Microeconomic Theory. New York: Oxford University Press. (Мас-Колелл А., Уинстон М., Грин Д. Микроэкономическая теория М.: Дело, 2016.)
Mauboussin, Michael. 2012. The Success Equation: Untangling Skill and Luck in Business. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
May, Robert M., Simon A. Levin, and George Sugihara. 2008. “Ecology for Bankers.” Nature 451: 893–895.
McCarty, Nolan. 2011. “Measuring Legislative Preferences.” In Oxford Handbook of Congress, ed. Eric Schickler and Frances Lee. New York: Oxford University Press.
McCarty, Nolan, and Adam Meirowitz. 2014. Political Game Theory: An Introduction. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
McKelvey, Richard. 1979. “General Conditions for Global Intransitivities in Formal Voting Models.” Econometnca 47: 1085–1112.
McPhee, William N. 1963. Formal Theories of Mass Behaviour. New York: Free Press of Glencoe.
Meadows, D., G. Meadows, J. Randers, and W. W Behrens III. 1972. The Limits to Growth. New York: Universe Books. (Медоуз Д., Медоуз Б. и т.д. и Йорген Рандерс. Пределы роста. М. : Издательство МГУ, 1991. Медоуз Д., Медоуз Б. и Рандерс Й. Пределы роста: 30 лет спустя. М. : Бином. Лаборатория знаний, 2016.)
Medin, Douglas, Will Bennis, and Michel Chandler. 2010. “The Home-Field Disadvantage.” Perspectives on Psychological Science 5, no. 6: 708–713.
Merriam, Daniel F., and John C. Davis. 2009. “Using Zipf’s Law to Predict Future Earthquakes in Kansas.” Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Science 112, nos. 1&2: 127–129.
Merton, Robert C. 1969. “Lifetime Portfolio Selection Under Uncertainty: The Continuous-Time Case.” Review of Economics and Statistics 51, no. 3: 247–257.
Merton, Robert K. 1963. “Resistance to the Systematic Study of Multiple Discoveries in Science.” European Journal of Sociology 4, no. 2: 237–282.
Milgrom, Paul, and John Roberts. 1986. “Pricing and Advertising Signals of Product Quality.” Journal of Political Economy 94, no. 4: 796–821.
Miller, John H. 1998. “Active Nonlinear Tests (ANTs) of Complex Simulation Models.” Management Science 44, no. 6: 820–830.
Miller, John H. 2015. A Crude Look at the Whole. New York: Basic Books.
Miller, John H., and Scott E. Page. 2004. “The Standing Ovation Problem.” Complexity 9, no. 5: 8–16.
Miller, John H., and Scott E. Page. 2007. Complex Adaptive Systems: An Introduction to Computational Modeb of Social Life. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Miller, Joshua B., and Adam Sanjurjo. 2015. “Surprised by the Gambler’s and Hot Hand Fallacies: A Truth in the Law of Small Numbers.” IGIER Working Paper no. 552.
Mitchell, Melanie. 1996. An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Mitchell, Melanie. 2009. Complexity: A Guided Tour. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Mlodinow, Leonard. 2009. The Drunkard’s Walk: How Randomness Rules Our Lives. New York: Penguin. (Леонард Млодинов. (Не)совершенная случайность. Как случай управляет нашей жизнью. М.: Гаятри/Livebook, 2013.)
Mokyr, Joel. 2002. The jpgts of Athena: Historical Origins of the Knowledge Economy. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. (Джоэль Мокир. Дары Афины. Исторические истоки экономики знаний. М.: Издательство Института Гайдара, 2012.)
Morgan, John, and Tanjim Hossain. 2006. ”… Plus Shipping and Handling: Revenue (Non)Equivalence in Field Experiments on eBay.” Advances in Economic Analysis & Policy 6, no. 2: 3.
Moss-Racusin, Corinne, John F. Dovidio, Victoria L. Brescoll, Mark J. Graham, and Jo Handelsman. 2012. “Science Faculty’s Subtle Gender Biases Favor Male Students.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1647–1649.
Munger, Charles. 1994. “A Lesson on Elementary, Worldly Wisdom as It Relates to Investment Management & Business.” University of Southern California Business School.
Murphy, Kevin M., and Robert H. Topel. 2016. “Human Capital Investment, Inequality and Growth.” Journal of Labor Economics 34: 99–127.
Murray, J. D. 1988. “Mammalian Coat Patterns: How the Leopard Gets Its Spots.” Scientific American 256: 80–87.
Myerson, Roger B. 1999. “On the Value of Game Theory in Social Science.” Rationality and Society 4: 62–73.
Myerson, Roger B. 1999. “Nash Equilibrium and the History of Economic Theory.” Journal of Economic Literature 37, no. 3: 1067–1082.
Nagel, Rosemarie. 1995. “Unraveling in Guessing Games: An Experimental Study.” American Economic Review 85, no. 5: 1313–1326.
Newman, Mark E. 2005. “Power Laws, Pareto Distributions and Zipf’s Law.” Contemporary Physics 46: 323–351.
Newman, Mark E. 2010. Networks: An Introduction. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Nowak, Martin. 2006. “Five Rules for the Evolution of Cooperation.” Science 314, no. 5805: 1560–1563.
Nowak, Martin A., and Karl Sigmund. 1998. “Evolution of Indirect Reciprocity by Image Scoring.” Nature 393: 573–577.
Olson, Mancur. 1965. The Logic of Collective Action: Public Goods and the Theory of Groups. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
O’Neil, Cathy 2016. Weapons of Math Destruction: How Big Data Increases Inequality and Threatens Democracy. New York, NY: Crown.
Open Science Collaboration. 2015. “Estimating the Reproducibility of Psychological Science.” Science 349: 6251.
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. 1996. The Knowledge Based Economy. Paris: OECD.
Ormerod, Paul. 2012. Positive Linking: How Networks Can Revolutionise the World. London: Faber and Faber.
Ostrom, Elinor. 2004. Understanding Institutional Diversity. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Ostrom, Elinor. 2010. “Beyond Markets and States: Polycentric Governance of Complex Economic Systems.” Transnational Corporations Review 2, no. 2: 1–12.
Ostrom, Elinor, Marco A. Janssen, and John M. Anderies. 2007. “Going Beyond Panaceas.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 104: 15176–15178.
Ostrovsky, Michael, Benjamin Edelman, and Michael Schwarz. 2007. “Internet Advertising and the Generalized Second Price Auction: Selling Billions of Dollars Worth of Keywords.” American Economic Review 97, no. 1: 242–259.
Paarsch, Harry J., and Bruce S. Shearer. 1999. “The Response of Worker Effort to Piece Rates: Evidence from the British Columbia Tree-Planting Industry.” Journal of Human Resources 34, no. 4: 643–667.
Packer, Craig, and Anne E. Pusey. 1997. “Divided We Fall: Cooperation Among Lions.” Scientific American, May, 52–59.
Paczuski, Maya, and Kai Nagel. 1996. “Self-Organized Criticality and 1// Noise in Traffic.” arXiv: cond-mat/9602011.
Page, Scott E. 1997. “An Appending Efficient Algorithm for Allocating Public Projects with Complementarities,” Journal of Public Economics 64, no 3: 291–322.
Page, Scott E. 2001. “Self Organization and Coordination.” Computational Economics 18: 25–48.
Page, Scott E. 2006. “Essay: Path Dependence.” Quarterly Journal of Political Science 1: 87–115.
Page, Scott E. 2007. The Difference: How the Power of Diversity Creates Better Groups, Teams, Schools, and Societies. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Page, Scott E. 2010a. Diversity and Complexity. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Page, Scott E. 2010b. “Building a Science of Economics for the Real World.” Presentation to the House Committee on Science and Technology Subcommittee on Investigations and Oversight, July 20.
Page, Scott E. 2012. “A Complexity Perspective on Institutional Design.” Politics, Philosophy and Economics 11: 5–25.
Page, Scott E. 2017. The Diversity Bonus. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Pan, Jessica. 2014. “ Gender Segregation in Occupations: The Role of Tipping and Social Interactions.” Journal of Labor Economics 33, no. 2: 365–408.
Parrish, Susan Scott. 2017. The Flood Year 1927: A Cultural History. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Parsa, H. G., John T. Self, David Njite, and Tiffany King. 2005. “Why Restaurants Fail.” Cornell Hospitality Quarterly 46, no. 3: 304–322.
Patel, Kayur, Steven Drucker, James Fogarty, Ashish Kapoor, and Desney Tan. 2011. “Using Multiple Models to Understand Data.” Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 1723–1728.
Peel, L. and A. Clauset. 2014. “Predicting Sports Scoring Dynamics with Restoration and Anti-Persistence.” Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Mining. Philadelphia: SIAM.
Pfeffer, Fabian T, and Alexandra Killewald. 2017. “Generations of Advantage: Multigenerational Correlations in Family Wealth.” Social Forces, 1–31.
Piantadosi, Steven. 2014. “Zipf’s Word Frequency Law in Natural Language: A Critical Review and Future Directions.” Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 21, no. 5: 1112–1130.
Pierson, Paul. 2004. Politics in Time: History, Institutions, and Social Analysis. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Piketty, Thomas. 2014. Capital in the 21st Century. Trans. Arthur Goldhammer. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press. (Тома Пикетти. Капитал в XXI веке. М.: Ad Marginem, 2015.)
Plott, C. R. 'A Notion of Equilibrium and its Possibility under Majority Rule', American Economic Review, 57 (1967), 787–806.
Pollack, John. 2014. Shortcut: How Analogies Reveal Connections, Spark Innovation, and Sell Our Greatest Ideas. New York: Gotham.
Poole, Keith T, and Howard Rosenthal. 1984. ‘A Spatial Model for Legislative Roll Call Analysis.” American Journal of Political Science 29, no. 2: 357–384.
Porter, David, and Vernon Smith. 2007. “FCC Spectrum Auction Design: A 12-Year Experiment.” Journal of Law, Economics, and Policy 3, no. 1: 63–80.
Powell, Robert. 1991. “Absolute and Relative Gains in International Relations Theory.” American Political Science Review 85, no. 4: 1303–1320.
Przeworski, Adam, Jose Antonio Cheibub, Michael E. Alvarez, and Fernando Limongi. 2000. Democracy and Development: Political Institutions and Material Well-Being in the World, 1950–1990. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Raby, Fiona. 2001. Design Noir: The Secret Life of Electronic Objects. Basel: Birkhauser.
Ramo, Joshua Cooper. 2016. The Seventh Sense: Power, Fortune, and Success, in the Age of Networks. New York: Little, Brown and Company.
Rand, David G., Hisashi Ohtsukia, and Martin A. Nowak. 2009. “Direct Reciprocity with Costly Punishment: Generous Tit-for-Tat Prevails.” Journal of Theoretical Biology 256, no. 1: 45–57.
Rapoport, Anatol. 1978. “Reality-Simulation: A Feedback Loop.” Sociocybernetics, 123–141.
Rauch, Jeffrey. 2012. Hyperbolic Partial Differential Equations and Geometric Optics. Graduate Studies in Mathematics. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society.
Rawls, John. 1971. A Theory of Justice. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. (Джон Ролз. Теория справедливости. — М.: Ленанд, 2017.)
Rescorla, Robert, and Allan Wagner. 1972. “A Theory of Pavlovian Conditioning: Variations in the Effectiveness of Reinforcement and Non-reinforcement.” In Classical Conditioning II, ed. A. H. Black and W F. Prokasy, 64–99. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Reynolds, Noel B., and Arlene Saxonhouse. 1994. Three Discourses. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Roberts, D. C, and D. L. Turcotte. 1998. “Fractality and Self-Organized Crit-icality of Wars.” Fractals 6: 351–357.
Roberts, Seth. 2004. “Self-Experimentation as a Source of New Ideas: Ten Examples About Sleep, Mood, Health, and Weight.” Behavioral and Brain Sciences 27, no. 2: 227–262.
Romer, Paul. 1986. “Increasing Returns and Long-Run Growth.” Journal of Political Economy 94: 1002–1037.
Rosen, Sherwin. 1981. “The Economics of Superstars.” American Economic Review 71: 845–858.
Roth, Alvin, and Ido Erev. 1995. “Learning in Extensive Form Games: Experimental Data and Simple Dynamic Models in the Intermediate Term.” Games and Economics Behavior 8: 164–212.
Russakoff, Dale. 2015. The Prize: Who’s in Charge of America’s Schools? Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
Rust, Jon. 1987. “Optimal Replacement of GMC Bus Engines: An Empirical Model of Harold Zurcher.” Econometrica 55, no. 5: 999–1033.
Ryall, Michael D., and Aaron Bramson. Inference and Intervention: Causal Models for Business Analysis. New York: Routledge.
Salganik, Matthew, Peter Dodds, and Duncan J. Watts. 2006. “Experimental Study of Inequality and Unpredictability in an Artificial Cultural Market.” Science 311: 854–856.
Samuelson, Paul. 1964. “Proof That Properly Anticipated Prices Fluctuate Randomly.” Industrial Management Review 6: 41–49.
Schrodt, Philip. 1998. “Pattern Recognition of International Crises Using Hidden Markov Models.” In Non-Linear Models and Methods in Political Science, ed. Diana Richards. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
Schwartz, Christine R., and Robert D. Mare. 2004. “Trends in Educational Assortative Marriage from 1940 to 2003.” Demography 42, no. 4: 621–646.
Schelling, Thomas. 1978. Micromotives and Macrobehavior. New York: W. W. Norton. (Шеллинг Т. Микромотивы и макровыбор. М. : Издательство Института Гайдара, 2016.)
Shiller, Robert. 2005. Irrational Exuberance. 2nd ed. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Scott, Steven L. 2010. “A Modern Bayesian Look at the Multi-Armed Bandit.” Applied Stochastic Models in Business and Industry 26: 639–658.
Shalizi, Cosma, and Andrew C. Thomas. 2011. “Homophily and Contagion Are Generically Confounded in Observational Social Network Studies.” Sociological Methods and Research 40: 211–239.
Shapiro, Thomas, Tatjana Meschede, and Sam Osoro. 2013. “The Roots of the Widening Racial Wealth Gap: Explaining the Black-White Economic Divide.” Research and Policy Brief, Institute on Assets and Social Policy, Brandeis University, Waltham, MA.
Shi, Xiaolin, Lada A. Adamic, Belle L. Tseng, and Gavin S. Clarkson. 2009. “The Impact of Boundary Spanning Scholarly Publications and Patents.” PLoS ONE 4, no. 8: e6547.
Silver, Nate. 2012. The Signal and the Noise: Why So Many Predictions Fail — but Some Don’t. New York: Penguin. (Сильвер Н. Сигнал и шум. Почему одни прогнозы сбываются, а другие — нет. — М.: КоЛибри, 2015.)
Simler, Kevin, and Robin Hanson. 2018. The Elephant in the Brain: Hidden Motives in Everyday Life. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Simmons, Matthew, Lada Adamic, and Eytan Adar. 2011. “Memes Online: Extracted, Subtracted, Injected, and Recollected.” Paper presented at the International Conference on Web and Social Media.
Slaughter, Ann Marie. 2017. The Chessboard and the Web: Strategies of Connection in a Networked World. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
Smaldino, Paul. 2013. “Measures of Individual Uncertainty for Ecological Models: Variance and Entropy.” Ecological Modelling 254: 50–53.
Small, Dana M., Robert J. Zatorre, Alain Dagher, Alan C. Evans, and Marilyn Jones-Gotman. 2001. “Changes in Brain Activity Related to Eating Chocolate: From Pleasure to Aversion.” Brain 124, no. 9: 1720–1733.
Smith, Eric, Rebecca Bliege Bird, and D. Bird. 2003. “The Benefits of Costly Signaling: Meriam Turtle Hunters.” Behavioral Ecology 14: 116–126.
Smith, Vernon. 2002. “Constructivist and Ecological Rationality.” Nobel Prize lecture. (Вернон Смит. Конструктивистская и экологическая рациональность в экономической науке. — МЭМ, т. V, кн. 2, стр. 755).
Sneppen, Kim, Per Bak, Henrik Flyvbjerg, and Mogens Jensen. 1994. “Evolution as a Self-Organized Critical Phenomenon.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 92: 5209–5213.
Solow, Robert M. 1956. “A Contribution to the Theory of Economic Growth.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 70, no. 1: 65–94.
Spence, A. Michael. 1973. ‘Job Market Signaling.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 87, no. 3: 355–374.
Squicciarini, Mara, and Nico Voigtlander. 2015. “Human Capital and Industrialization: Evidence from the Age of Enlightenment.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 30, no. 4: 1825–1883.
Starfield, Anthony, Karl Smith, and Andrew Bleloch. 1994. How to Model It: Problem Solving for the Computer Age. Minneapolis, MN: Burgess International.
Stein, Richard A. 2011. “Superspreaders in Infectious Diseases.” International Journal of Infectious Diseases 15, no. 8: e510-e513.
Sterman, John D. 2000. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Sterman, John. 2006. “Learning from Evidence in a Complex World.” American Journal of Public Health 96, no. 3: 505–515.
Stiglitz, Joseph. 2013. The Price of Inequality: How Today’s Divided Society Endangers Our Future. New York: W W Norton. (Стиглиц дж.. Цена неравенства. Чем расслоение общества грозит нашему будущему. М.: Эксмо, 2015.)
Stock, James H., and Mark W. Watson. 2003. “Has the Business Cycle Changed and Why?” In National Bureau of Economic Research Macroeconomics Annual 2002, vol. 17, ed. Mark Gertler and Kenneth Rogoff, 159–218. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Stone, Lawrence D., Colleen M. Keller, Thomas M. Kratzke, and Johan E. Strumpfer. 2014. “Search for the Wreckage of Air France Flight AF 447.” Statistical Science 29, no. 1: 69–80.
Storchmann, Karl. 2011. “Wine Economics: Emergence, Developments, Topics.” Agrekon 50, no. 3: 1–28.
Suki, Bela, and Urs Frey. 2017. “A Time Varying Biased Random Walk Model of Growth: Application to Height from Birth to Childhood.” Journal of Critical Care 38: 362–370.
Suroweicki, James. 2006. The Wisdom of Crowds. New York: Anchor Press. (Шуровьески Дж.. М. : Манн, Иванов и Фербер, 2013.)
Syverson, Chad. 2007. “Prices, Spatial Competition, and Heterogeneous Producers: An Empirical Test.” Journal of Industrial Economics 55, no. 2: 197–222.
Taleb, Nassim. 2001. Fooled by Randomness. New York: Random House. (Талеб Н. М. : Манн, Иванов и Фербер, 2018.)
Taleb, Nassim. 2007. The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable. New York: Random House. (Талеб Н. Черный лебедь. Под знаком непредсказуемости. Азбука Аттикус, КоЛибри, 2018.)
Taleb, Nassim. 2012. Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder. New York: Random House. (Талеб Н. Антихрупкость. Как извлечь выгоду из хаоса. КоЛибри, 2016.)
Tassier, Troy. 2013. The Economics of Epidemiology. Amsterdam: Springer.
Tetlock, Phillip. 2005. Expert Political Judgment: How Good Is It? How Can We Know? Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Thaler, R. H. 1981. “Some Empirical Evidence on Dynamic Inconsistency.” Economic Letters 8, no. 3: 201–207.
Thompson, Derek. 2014. “How You, I, and Everyone Got the Top 1 Percent All Wrong: Unveiling the Real Story Behind the Richest of the Rich.” Atlantic, March 30.
Thorndike, Edward L. 1911. Animal Intelligence. New York: Macmillan.
Tilly, Charles. 1998. Durable Inequality. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Tsebelis, George. 2002. Veto Players: How Political Institutions Work. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Turchin, Peter. 1998. Quantitative Analysis of Movement: Measuring and Modeling Population Redistribution in Animals and Plants. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates.
Tweedle, Valerie, and Robert J. Smith. 2012. “A Mathematical Model of Bieber Fever: The Most Infectious Disease of Our Time?” In Understanding the Dynamics of Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases Using Mathematical Models,, ed. Steady Mushayabasa and Claver P. Bhunu. Cham, Switzerland: Springer.
Ugander, Johan, Brian Karrer, Lars Backstrom, and Cameron Marlow. 2011. “The Anatomy of the Facebook Social Graph.” arXiv:1111.4503.
Updike, John. 1960. “Hub Fans Bid Kid Adieu.” New Yorker, October 22.
US Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2013. Consumer Expenditures in 2011. Report 1042, April. Washington, DC: BLS.
Uzzi, Brian, Satyam Mukherjee, Michael Stringer, and Ben Jones. 2013. “Atypical Combinations and Scientific Impact.” Science 342: 468–471.
Van Noorden, Richard. 2015. “Interdisciplinary Research by the Numbers.” Nature, September 16.
von Neumann, John, and Morgenstern, Oskar. 1953. Theory of Games and Economic Behavior. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. (Джон фон Нейман, Оскар Моргенштерн. Теория игр и экономическое поведение. М.: Наука, 1970).
Vriend, Nicolaas J. 2000. “An Illustration of the Essential Difference Between Individual and Social Learning, and Its Consequences for Computational Analyses.” Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 24: 1–19.
Wainer, Howard. 2009. Picturing the Uncertain World. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Wakeland, W, A. Nielsen, and E Geissert. 2015. “Dynamic Model of Non-medical Opioid Use Trajectories and Potential Policy Interventions.” American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 41, no. 6: 508–518.
Waltz, Kenneth. 1979. Theory of International Politics. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Washington Post. 2012. “Mad Money: TV Ads in the 2012 Presidential Campaign.” .
Watts, Duncan. 2011. Everything Is Obvious Once You Know the Answer. New York: Crown Business.
Watts, Duncan, and Steven Strogatz. 1998. “Collective Dynamics of’Small-World’ Networks.” Nature 393, no. 6684: 440–442.
Weisberg, Michael. 2007. “Three Kinds of Idealization.” Journal of Philosophy 104, no. 12: 639–659.
Weisberg, Michael. 2012. Simulation and Similarity: Using Models to Understand the World. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Weisberg, Michael, and Muldoon, Ryan. 2009. “Epistemic Landscapes and the Division of Cognitive Labor.” Philosophy of Science 76, no. 2: 225–252.
Weitzman, Martin L. 1979. “Optimal Search for the Best Alternative.” Econometrica 77: 641–654.
Weitzman, Martin L. 1998. “Recombinant Growth.” Quarterly Journal of Economics 2: 331–361.
Wellman, Michael. 1990. “Fundamental Concepts of Qualitative Probabilistic Networks.” Artificial Intelligence 44: 257–303.
Wellman, Michael. 2013. “Head to Head: Does US High-Frequency Trading Need Stricter Regulatory Oversight? (YES).” International Financial Law Review, September.
West, Geoffrey. 2017. Scale: The Universal Laws of Growth, Innovation, Sus-tainability, and the Pace of Life in Organisms, Cities, Economies, and Companies. New York: Penguin. (Уэст Дж.. Масштаб. Универсальные законы роста, инноваций, устойчивости и темпов жизни организмов, городов, экономических систем и компаний. М. : Азбука, 2018.)
Whittle, Peter. 1979. “Discussion of Dr Gittins’ Paper.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 41, no. 2: 148–177.
Whitty, Robin W. 2017. “Some Comments on Multiple Discovery in Mathematics.” Journal of Humanistic Mathematics 7, no. 1: 172–188.
Wigner, Eugene. 1960. “The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Mathematics in the Natural Sciences.” Communications in Pure and Applied Mathematics 13, no. 1. (Вигнер Е.. Инвариантность и законы сохранения. Этюды о симметрии. Ленанд, 2015.)
Wilkinson, Richard, and Kate Pickett. 2009. The Spirit Level: Why Greater Equality Makes Societies Stronger. London: Bloomsbury.
Wilson, David Sloan. 1975. “A Theory of Group Selection.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 72, no. 1: 143–146.
Wolfram, Stephen. 2001. A New Kind of Science. Champaign, IL: Wolfram Media.
Wright, Robert. 2001. Nonzero: The Logic of Human Destiny. New York: Vintage.
Wu, Jianzhong, and Robert Axelrod. 1995. “How to Cope with Noise in the Iterated Prisoner’s Dilemma.” Journal of Conflict Resolution 39, no. 1: 183–189.
Wuchty Stefan, Benjamin F. Jones, and Brian Uzzi. 2007. “The Increasing Dominance of Teams in the Production of Knowledge.” Science 316, no. 5827: 1036–1039.
Xie, Yu. 2007. “Otis Dudley Duncan’s Legacy: The Demographic Approach to Quantitative Reasoning in Social Science.” Research in Social Stratification and Mobility 25: 141–156.
Xie, Yu, Alexandra Killewald, and Christopher Near. 2016. “Between- and Within-Occupation Inequality: The Case of High Status Professions.” Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science 663, no. 1: 53–79.
Youn, Hyejin, Deborah Strumsky, Luis Bettencourt, and Jose Lobo. 2015. “Inventions as a Combinatorial Process: Evidence From US Patents.” Journal of the Royal Society Interfaces 12: 0272.
Zagorsky, Jay. 2007. “Do You Have to Be Smart to Be Rich? The Impact of IQ on Wealth, Income and Financial Distress.” Intelligence 35: 489–501.
Zahavi, Amotz. 1974. “Mate Selection: A Selection for a Handicap.” Journal of Theoretical Biology 53, no. 1: 205–214.
Zak, Paul, and Stephen Knack. 2001. “Trust and Growth.” Economic Journal 111, no. 470: 295–321.
Zaretsky, Adam. 1998. “Have Computers Made Us More Productive? A Puzzle.” Regional Economist, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
Ziliak, Stephen T., and Deirdre N. McCloskey. 2008. The Cult of Statistical Significance: How the Standard Error Costs Us Jobs, Justice, and Lives. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.

